
一、 🏞️创建源码分析环境
1. 创建一个 vue 项目
npm init vue@latest
# or
yarn create vite
2. Pinia 源码入口
🚗源码地址: github.com/vuejs/pinia
📦打包文件: rollup.config.js
🚪入口文件: packages/pinia/src/index.ts
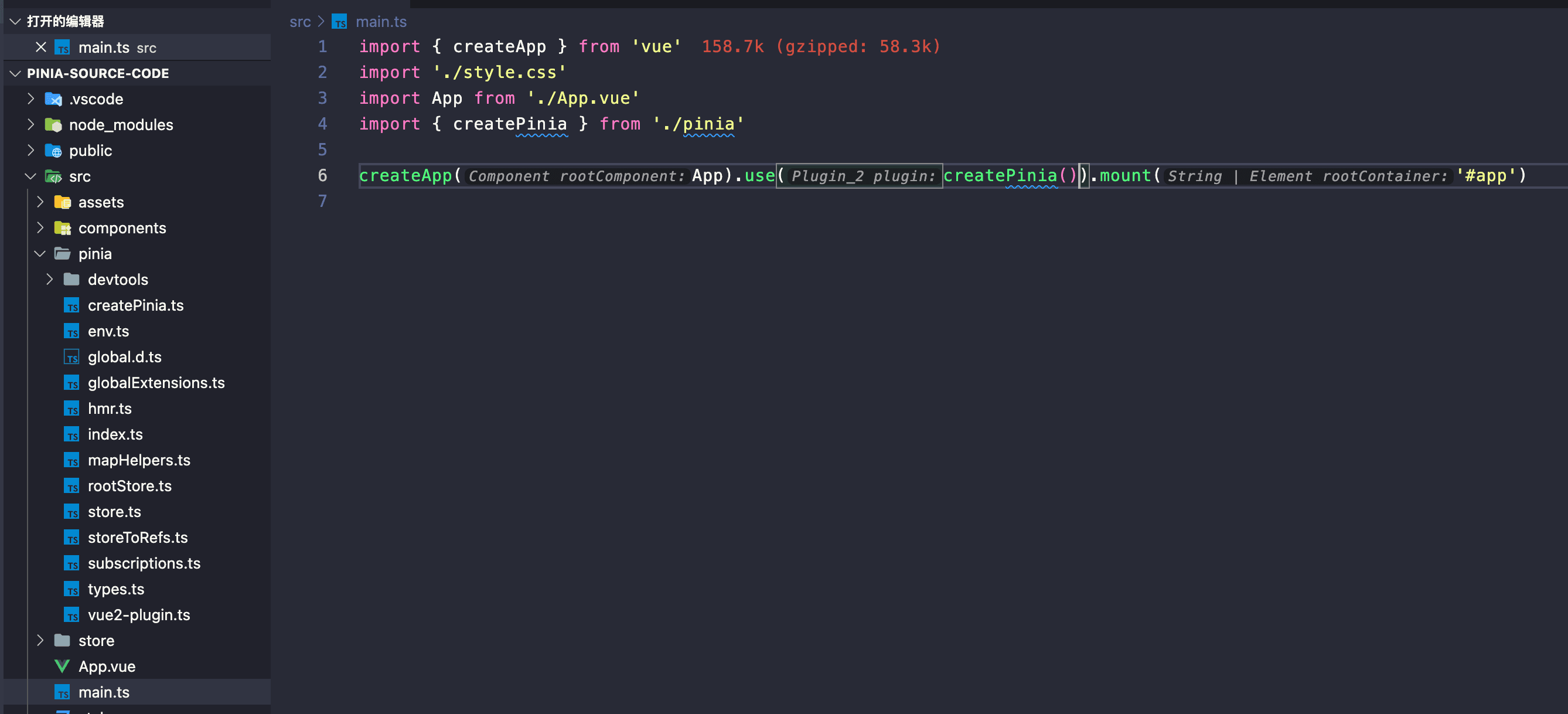
3. 复制 Pinia 源码 & 在 main.ts 中初始化 Pinia 插件
将 pinia/packages/pinia/src 目录下的所有文件复制到我们之前生成项目的/src/pinia 中。
在 main.ts 中安装初始化 Pinia:
4. 添加必要仓库依赖
此时通过 yarn dev 启动项目时,会报缺少依赖。
在 rollup.config.js 第122行,可以看到依赖分别有
vue-demi:一个可以帮助我们开发在vue2、vue3上通用的 vue 库的开发工具。vue:vue 项目。@vue/composition-api:vue 组合式 api 插件。
121 | const external = ['vue-demi', 'vue', '@vue/composition-api']
在我们的项目中安装好这两个库(vue 在创建项目时已经安装了)。
yarn add vue-demi @vue/composition-api
5. 添加必要环境变量
此时通过 yarn dev 启动项目时,会报饮用错误。
Uncaught ReferenceError: __DEV__ is not defined
at rootStore.ts:97:3
环境变量位于 rollup.config.js 第167行:
const replacements = {
__COMMIT__: `"${process.env.COMMIT}"`,
__VERSION__: `"${pkg.version}"`,
__DEV__:
(isBundlerESMBuild && !isRawESMBuild) || (isNodeBuild && !isProduction)
? // preserve to be handled by bundlers
`(process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production')`
: // hard coded dev/prod builds
JSON.stringify(!isProduction),
// this is only used during tests
__TEST__:
(isBundlerESMBuild && !isRawESMBuild) || isNodeBuild
? `(process.env.NODE_ENV === 'test')`
: 'false',
__FEATURE_PROD_DEVTOOLS__: isBundlerESMBuild
? `(typeof __VUE_PROD_DEVTOOLS__ !== 'undefined' && __VUE_PROD_DEVTOOLS__)`
: 'false',
// If the build is expected to run directly in the browser (global / esm builds)
__BROWSER__: JSON.stringify(isRawESMBuild),
// is targeting bundlers?
__BUNDLER__: JSON.stringify(isBundlerESMBuild),
__GLOBAL__: JSON.stringify(isGlobalBuild),
// is targeting Node (SSR)?
__NODE_JS__: JSON.stringify(isNodeBuild),
}
我们在 vite.config.ts 中添加缺少的环境变量:
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [vue()],
define: {
__DEV__: true,
__TEST__: true
}
})
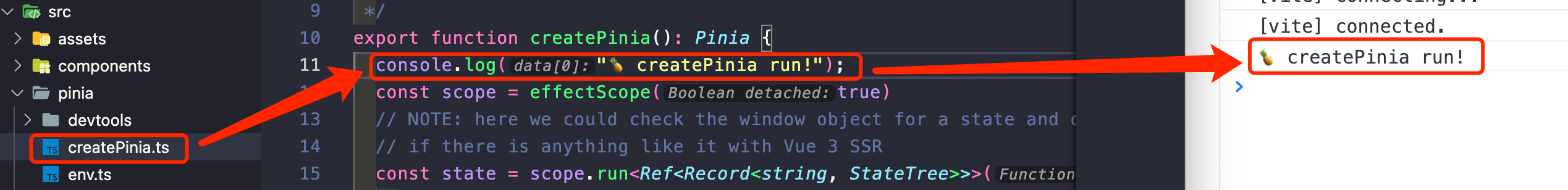
6. 环境测试
在 src/pinia/createPinia.ts 中输出字符串,查看控制台是否正常打印,如正常打印则源码分析环境正常运行:
二、🧐源码分析(1)——执行流程
在 defineStore、 createPinia、 useStore 等关键函数内打印日志来确定执行顺序:

可以确定执行顺序为:
defineStore() ⇒ main.ts ⇒ createPinia() ⇒ useStore()
其中 defineStore() 是在引用阶段被调用,并返回 useStore() 函数,之后便开始 Vue 的流程。注册插件等,最后在页面内调用 useStore(),创建 Store 等步骤。
三、🧐源码分析(2)——createPinia
使用 Pinia 前需要在 vue 中初始化一个注册 Pinia,注册的方法是使用 :
import { createPinia } from 'pinia';
app.use(createPinia());
显然 createPinia 函数返回的是一个 vue插件 。通过插件的方式安装到 vue 中。
1. 源码目录
在 src/pinia/index.ts 目录中可以找到:
export { createPinia } from './createPinia'
显然 createPinia 函数的源码目录为: src/pinia/createPinia.ts 。
2. createPinia
在函数的最开始,通过 effectScope 声明了一个 ref,并赋值给了state,我们将其 简单理解为声明了一个 ref 并赋值给 state 。
import { Pinia, PiniaPlugin, setActivePinia, piniaSymbol } from './rootStore';
import { ref, App, markRaw, effectScope, isVue2, Ref } from 'vue-demi';
import { registerPiniaDevtools, devtoolsPlugin } from './devtools';
import { USE_DEVTOOLS } from './env';
import { StateTree, StoreGeneric } from './types';
/**
* 创建应用程序要使用的Pinia实例
*/
export function createPinia(): Pinia {
console.log('🍍 createPinia run!');
/**
* effectScope:
* 创建一个 effect 作用域,可以捕获其中所创建的响应式副作用 (即计算属性和侦听器),这样捕获到的副作用可以一起处理。对于该 API 的使用细节,请查阅对应的 RFC。
*/
const scope = effectScope(true);
// NOTE: 在这里,我们可以检查窗口对象的状态,并直接设置它
// 如果有类似Vue 3 SSR的东西
const state = scope.run<Ref<Record<string, StateTree>>>(() => ref<Record<string, StateTree>>({}))!;
// 所有需要安装的插件
let _p: Pinia['_p'] = [];
// 在调用 app.use(pinia) 前需要安装的插件
let toBeInstalled: PiniaPlugin[] = [];
// 使用 markRaw 包裹的 pinia 使其不会变为响应式
const pinia: Pinia = markRaw({
// app.use 执行的逻辑
install(app: App) {
// 设置当前使用的 pinia 实例
setActivePinia(pinia);
// 如果是 vue2 ,全局注册已经在 PiniaVuePlugin 完成,所以这段逻辑将跳过
if (!isVue2) {
// app 实例
pinia._a = app;
// 通过 provide 传递 pinia 实例,提供给后续使用
app.provide(piniaSymbol, pinia);
// 设置全局属性 $pinia
app.config.globalProperties.$pinia = pinia;
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (USE_DEVTOOLS) {
registerPiniaDevtools(app, pinia);
}
// 处理未执行插件
toBeInstalled.forEach((plugin) => _p.push(plugin));
// 处理完插件后清空
toBeInstalled = [];
}
},
/**
* 为 Pinia 提供安装插件的能力
* @param plugin
* @returns Pinia
*/
use(plugin) {
// 如果 use 阶段初始化完成则暂存 toBeInstalled 中
if (!this._a && !isVue2) {
toBeInstalled.push(plugin);
} else {
_p.push(plugin);
}
return this;
},
_p, // 所有的 pinia 插件
// it's actually undefined here
// @ts-expect-error
_a: null, // vue 实例,在 install 阶段设置
_e: scope, // pinia 的作用域对象,每个 store 都有单独的 scope
_s: new Map<string, StoreGeneric>(), // store 缓存,key 为 pinia 的 id,value 为 pinia 对外暴漏的数据
state, // pinia 所有的 state 的合集,key 为 pinia 的 id,value 为 store 下所有的 state
});
// pinia devtools rely on dev only features so they cannot be forced unless
// pinia开发工具依赖于仅用于开发的功能,因此除非
// the dev build of Vue is used. Avoid old browsers like IE11.
// 使用Vue的开发版本。避免使用像IE11这样的旧浏览器。
if (USE_DEVTOOLS && typeof Proxy !== 'undefined') {
pinia.use(devtoolsPlugin);
}
return pinia;
}
四、🧐源码分析(3)——defineStore
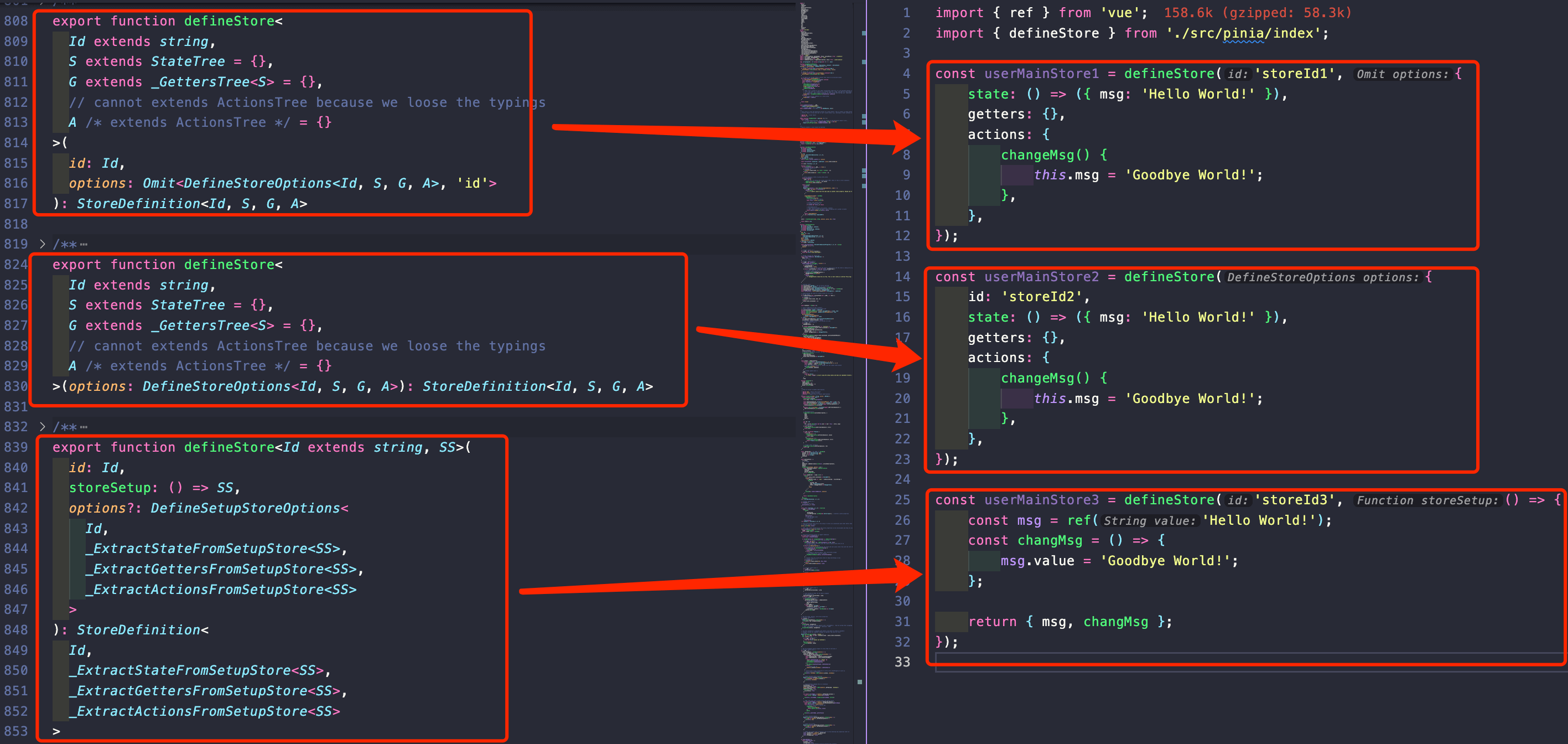
1. 三种创建方式
defineStore 所在位置: src/pinia/store.ts 进入文件之后可以看到通过函数重载的方式提供给我们三种参数传递方式:
其中参数含义如下:
id:store 的 id,必须唯一。options: 与 Vue 的选项式 API 类似,我们也可以传入一个带有id、state、actions与getters属性的 Option 对象。storeSetup:以setup的方式创建,与 Vue 的 setup 函数 相似。在 storeSetup 中:ref()等同于state。computed()等同于getters。function()等同于actions。
2. defineStore 的执行逻辑
在 defineStore 函数中,并没有很特别的逻辑,首先是对三种创建方式进行兼容,然后定义一个名为 useStore 的函数,然后返回 useStore。
useStore 具体做了什么下节分析。
export function defineStore(
// TODO: add proper types from above
idOrOptions: any,
setup?: any,
setupOptions?: any
): StoreDefinition {
let id: string
let options:
| DefineStoreOptions<
string,
StateTree,
_GettersTree<StateTree>,
_ActionsTree
>
| DefineSetupStoreOptions<
string,
StateTree,
_GettersTree<StateTree>,
_ActionsTree
>
// 此处对三种创建方式进行兼容处理
const isSetupStore = typeof setup === 'function'
if (typeof idOrOptions === 'string') {
id = idOrOptions
// the option store setup will contain the actual options in this case
options = isSetupStore ? setupOptions : setup
} else {
options = idOrOptions
id = idOrOptions.id
}
// useStore
function useStore(pinia?: Pinia | null, hot?: StoreGeneric): StoreGeneric {
// ...
}
useStore.$id = id;
// 将 useStore 函数返回出去,但不会立即调用,在组件内使用 store 时才会调用。
// 所以在 defineStore 中只是做了些兼容逻辑,然后返回一个函数,返回的这个函数真正调用时才会触发更多逻辑。
return useStore;
}
虽然我们前面定义了一个 store,但在我们使用 <script setup> 调用 useStore() (或者使用 setup() 函数,像所有的组件那样) 之前,store 实例是不会被创建的。
<script setup>
import { useMainStore1 } from '@/stores/counter'
// 可以在组件中的任意位置访问 `store` 变量 ✨
const store = useMainStore1();
</script>
4. useStore
在之前我们分析了 defineStore 方法调用的时候返回了 useStore 方法,接下来看一下此方法究竟干了些什么。
function useStore(pinia?: Pinia | null, hot?: StoreGeneric): StoreGeneric {
Log('useStore()');
// 获取当前 vue 实例
const currentInstance = getCurrentInstance();
pinia =
// 在 test 模式下,忽略提供的参数,因为我们总是可以通过 getActivePinia() 获取 pinia 实例
// 如果 是test模式 && activePinia不为空 && activePinia是test模式 则为空 否则 返回参数中的pinia
// 或者 如果获取到了当前实例 并且 存在piniaSymbol 返回 inject(piniaSymbol, null) 否则 返回空
(__TEST__ && activePinia && activePinia._testing ? null : pinia) ||
// 这里的 inject(piniaSymbol) 是在 createPinia 的 install 中 app.provide(piniaSymbol, pinia);
(currentInstance && inject(piniaSymbol, null));
console.log('pinia 实例 ==>', pinia);
// 将当前 pinia 实例设置为激活的 pinia
// 如果存在多个 pinia 实例,方便后续逻辑获取当前pinia实例
if (pinia) setActivePinia(pinia);
// 在 dev环境 并且 获取不到当前 pinia 实例,则说明未全局注册,抛出错误
if (__DEV__ && !activePinia) {
throw new Error(`[🍍]: getActivePinia was called with no active Pinia. Did you forget to install pinia?\n` + `\tconst pinia = createPinia()\n` + `\tapp.use(pinia)\n` + `This will fail in production.`);
}
// 将激活的 pinia 实例赋值给 pinia 变量,确保 pinia === activePinia。防止 setActivePinia 出错导致两个变量不一致
pinia = activePinia!;
// 如果 pinia 的 store 缓存中没有当前的 id,则创建新的 store,
// 否则直接获取缓存中 store。
if (!pinia._s.has(id)) {
// 创建 store 并将其注册在 pinia._s 中
if (isSetupStore) {
// 组合式
createSetupStore(id, setup, options, pinia);
} else {
// 选项式
createOptionsStore(id, options as any, pinia);
}
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (__DEV__) {
// @ts-expect-error: not the right inferred type
useStore._pinia = pinia;
}
}
// 获取 pinia 缓存中的 store
const store: StoreGeneric = pinia._s.get(id)!;
// 开发环境 并且 是热更新
if (__DEV__ && hot) {
const hotId = '__hot:' + id;
const newStore = isSetupStore ? createSetupStore(hotId, setup, options, pinia, true) : createOptionsStore(hotId, assign({}, options) as any, pinia, true);
hot._hotUpdate(newStore);
// cleanup the state properties and the store from the cache
delete pinia.state.value[hotId];
pinia._s.delete(hotId);
}
// save stores in instances to access them devtools
if (
__DEV__ &&
IS_CLIENT &&
currentInstance &&
currentInstance.proxy &&
// avoid adding stores that are just built for hot module replacement
!hot
) {
const vm = currentInstance.proxy;
const cache = '_pStores' in vm ? vm._pStores! : (vm._pStores = {});
cache[id] = store;
}
// StoreGeneric cannot be casted towards Store
return store as any;
}
从上边代码中,可以发现最关键的两个函数是 createSetupStore、 createOptionsStore,分别是创建 组合式Store 和 选项式Store。里边包含了创建 store 的关键逻辑,下面分别来看一下。
5. createSetupStore
createSetupStore 的作用是创建一个组合式的 store,之后的 createOptionsStore 其实也是把 option 转化后调用 createSetupStore 来创建 store。createSetupStore 的源码很长,我们分批研究。对于一些变量的定义等内容在此省略,只关注最核心逻辑,详细的注释可以查看 Github 中的源码。
(1) 参数
createSetupStore 总共接收了6个参数:
- $id :当前 Store 的 ID,
- setup defineStore 或者 createOptionsStore 传入的 setup 函数
- options 配置选项,state、getter、actions 等
- pinia Pinia 实例
- hot 热更新相关
- isOptionsStore 是否是 选项式 Store 创建
/**
* 创建组合式 Store
* @param $id Store ID
* @param setup defineStore 传入的 setup 函数
* @param options 配置选项
* @param pinia Pinia 实例
* @param hot 热更新相关
* @param isOptionsStore 是否是 选项式 Store 创建
* @returns 创建的 store
*/
function createSetupStore<Id extends string, SS extends Record<any, unknown>, S extends StateTree, G extends Record<string, _Method>, A extends _ActionsTree>($id: Id, setup: () => SS, options: DefineSetupStoreOptions<Id, S, G, A> | DefineStoreOptions<Id, S, G, A> = {}, pinia: Pinia, hot?: boolean, isOptionsStore?: boolean): Store<Id, S, G, A> {
// ...
return store;
}
(2) 创建 Store
此过程中,创建一个 setupStore 常量,创建了一个作用域并执行了 setup 函数,获取到 setup 函数中返回的内容,也就是我们定义的 state、getter、action 等内容。
在此过程中,state 的内容也会被存储到 pinia.state 中。action 则会被 wrapAction 处理。
对每一项 action 进行处理,目的是为了支持 $onAction 方法,此方法会在执行 action 时执行回调函数,回调函数可以接收三个参数分别是:被调用的 store、action 的名字、传递给 action 的参数。在 store 中还会有一些基础操作的 API ,请看下节。
// 在当前 pinia 实例的缓存中新建一个作用域,在作用域中执行 setup 函数
// 执行的结果为 store 。 example: { count: ObjectRefImpl, increment: Function () }
const setupStore = pinia._e.run(() => {
scope = effectScope();
return scope.run(() => setup());
})!;
// 覆盖现有操作以支持 $onAction
for (const key in setupStore) {
const prop = setupStore[key];
// ((如果是 ref) 并且 (不是 computed)) 或者 (是 reactive)
if ((isRef(prop) && !isComputed(prop)) || isReactive(prop)) {
// 如果是 optionsStore 方式创建,option 结构已经在 createOptionsStore 将其加入 pinia
if (!isOptionsStore) {
// 将 ref 转移到 pinia state 以保持一切同步
if (isVue2) {
set(pinia.state.value[$id], key, prop);
} else {
pinia.state.value[$id][key] = prop;
}
}
// 否则,如果是函数类型,那么它就是一个 action
} else if (typeof prop === 'function') {
// 如果是重写这个值,应该避免使用 wrapAction 重复包装
const actionValue = __DEV__ && hot ? prop : wrapAction(key, prop);
// 这是一个热更新模块替换 store,因为 hotUpdate 方法需要在正确的上下文中执行它
if (isVue2) {
set(setupStore, key, actionValue);
} else {
setupStore[key] = actionValue;
}
// 将 actions 存储到插件配置的 actions 数组,以便它们可以在插件中使用
optionsForPlugin.actions[key] = prop;
}
}
(3) 基础 API
在 Pinia 的 store 中存在很多基础 API,比如:获取 store id $id、增加 action 调用回调 $onAction()、重置 store $reset()、变更 store $patch()、订阅 $subscribe()、移除 store $dispose、获取所有 state $state 等。我们逐个分析。
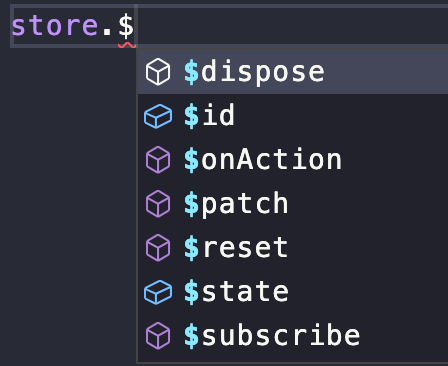
基础的 API 首先被储存在 partialStore 中,然后创建一个 store 常量,并且把这些基础 API 和 store 的内容都合并到 store 常量中。
/**
* 具有 state 和 功能 的基本 store,但不能直接使用。
*/
const partialStore = {
_p: pinia,
$id,
$onAction,
$patch,
$reset,
$subscribe,
$dispose,
} as _StoreWithState<Id, S, G, A>;
(4) Store 和 基础 API 合并
在 (2) 和 (3) 中我们创建了 store 的基本内容和基础的API,现在新建一个变量,并把它们合并到一块:
/**
* 创建一个响应式的 store 对象
* 将基础函数合并到 store 中
*/
const store: Store<Id, S, G, A> = reactive(
__DEV__ || USE_DEVTOOLS
? assign(
{
_hmrPayload,
_customProperties: markRaw(new Set<string>()), // devtools custom properties
},
partialStore
// must be added later
// setupStore
)
: partialStore
) as unknown as Store<Id, S, G, A>;
assign(toRaw(store), setupStore)
现在,还缺少一个获取所有 state 得属性: $state ,我们使用 defineProperty 给 store 增加 $state 属性 :
// 使用它而不是 computed with setter 可以在任何地方创建它,而无需将计算的生命周期链接到首次创建 store 的任何地方。
// 给 store 定义 $state 属性,方便获取全部的 state
Object.defineProperty(store, '$state', {
get: () => (__DEV__ && hot ? hotState.value : pinia.state.value[$id]),
set: (state) => {
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (__DEV__ && hot) {
throw new Error('cannot set hotState');
}
$patch(($state) => {
assign($state, state);
});
},
});
(5) 对于 Pinia 自定义插件的处理
在之前的 createPinia() 方法中,Pinia 实例上存在一个 use() 方法是对自定义插件的支持,在这里我们需要对安装的插件进行处理,调用左右的插件函数,并给函数传入 store app piain options 四个参数。
// apply 全部插件
pinia._p.forEach((extender) => {
console.log("插件安装:", extender);
// 如果使用开发工具
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (USE_DEVTOOLS) {
const extensions = scope.run(() =>
// 调用插件,并传入参数
extender({
store,
app: pinia._a,
pinia,
options: optionsForPlugin,
})
)!;
Object.keys(extensions || {}).forEach((key) => store._customProperties.add(key));
assign(store, extensions);
} else {
// 这里将插件返回的属性合并到 store 中
assign(
store,
scope.run(() =>
extender({
store,
app: pinia._a,
pinia,
options: optionsForPlugin,
})
)!
);
}
});
我们可以这样给 Piain 安装插件:
const pinia = createPinia();
// 给 pinia 安装插件
pinia.use((prop) => {
Log('Pinia 插件使用');
console.log('插件获取到的参数:', prop);
return {
$aaa: (param: string) => {
console.log('这里是插件安装到 Pinia 上的功能');
console.log('prop', prop);
console.log('param', param);
},
};
});
app.use(pinia);
使用插件:
store.$aaa('传递的参数');

6. createOptionsStore
createOptionsStore 的代码量比较少,从下面的代码可以发现,基本的逻辑就是从 options 中获取到 state、 actions、 getters,定义一个 setup 函数并调用 createSetupStore 创建 Store,还要将 getters 转换为 computed。
/**
* 创建 选项式 store
* @param id Store ID
* @param options 配置选项
* @param pinia Pinia 实例
* @param hot 热更新相关
* @returns 创建的 store
*/
function createOptionsStore<Id extends string, S extends StateTree, G extends _GettersTree<S>, A extends _ActionsTree>(id: Id, options: DefineStoreOptions<Id, S, G, A>, pinia: Pinia, hot?: boolean): Store<Id, S, G, A> {
Log('createOptionsStore()');
const { state, actions, getters } = options;
const initialState: StateTree | undefined = pinia.state.value[id];
let store: Store<Id, S, G, A>;
/**
* 自定义一个 setup 函数
* @returns store
*/
function setup() {
if (!initialState && (!__DEV__ || !hot)) {
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (isVue2) {
set(pinia.state.value, id, state ? state() : {});
} else {
pinia.state.value[id] = state ? state() : {};
}
}
// 避免在 pinia.state.value 中创建 state
const localState =
__DEV__ && hot
? // 使用 ref() 解包状态中的引用
toRefs(ref(state ? state() : {}).value)
: toRefs(pinia.state.value[id]);
return assign(
localState,
actions,
Object.keys(getters || {}).reduce((computedGetters, name) => {
if (__DEV__ && name in localState) {
// getter 不能和 state 属性同名
console.warn(`[🍍]: A getter cannot have the same name as another state property. Rename one of them. Found with "${name}" in store "${id}".`);
}
// 把 getter 转为 computed
computedGetters[name] = markRaw(
computed(() => {
setActivePinia(pinia);
// it was created just before
const store = pinia._s.get(id)!;
// allow cross using stores
/* istanbul ignore next */
if (isVue2 && !store._r) return;
// @ts-expect-error
// return getters![name].call(context, context)
// TODO: avoid reading the getter while assigning with a global variable
return getters![name].call(store, store);
})
);
return computedGetters;
}, {} as Record<string, ComputedRef>)
);
}
store = createSetupStore(id, setup, options, pinia, hot, true);
return store as any;
}
五、🧐源码分析(4)—— store 的基础 API 实现
1. $id
这个没啥好说的,就是 createSetupStore 参数中的 $id。
2. $onAction
设置一个回调,当一个 action 即将被调用时,就会被调用。 回调接收一个对象, 其包含被调用 action 的所有相关信息:
store: 被调用的 storename: action 的名称args: 传递给 action 的参数
除此之外,它会接收两个函数, 允许在 action 完成或失败时执行的回调。
它还会返回一个用来删除回调的函数。 请注意,当在组件内调用 store.$onAction() 时,除非 detached 被设置为 true, 否则当组件被卸载时,它将被自动清理掉。
在 Pinia 的源码中,关于 $onAction 的代码是这样的:
const partialStore = {
// ...
$onAction: addSubscription.bind(null, actionSubscriptions),
// ...
}
可以发现, $onAction 就是给 addSubscription 函数绑定了个 null 的 this 和一个参数,再来看一下这个 addSubscription 是何方神圣:
export const noop = () => {};
/**
* 添加订阅
* @param subscriptions 订阅者数组
* @param callback 回调
* @param detached
* @param onCleanup 当清楚订阅时的回调
* @returns 清除订阅的回调
*/
export function addSubscription<T extends _Method>(
subscriptions: T[],
callback: T,
detached?: boolean,
onCleanup: () => void = noop
) {
subscriptions.push(callback);
// 移除订阅
const removeSubscription = () => {
const idx = subscriptions.indexOf(callback);
// 如果存在这个订阅,在订阅数组中移除掉,并执行回调
if (idx > -1) {
subscriptions.splice(idx, 1);
// 执行移除订阅回调
onCleanup();
}
};
// detached 为 true 时,在当前作用于停止时,不会删除此订阅,为 false 时会移除此订阅
// getCurrentScope 如果有的话,返回当前活跃的 effect 作用域
if (!detached && getCurrentScope()) {
// onScopeDispose: 在当前活跃的 effect 作用域上注册一个处理回调函数。当相关的 effect 作用域停止时会调用这个回调函数。
onScopeDispose(removeSubscription);
}
// 返回移除订阅的函数
return removeSubscription;
}
3. $patch
将一个 state 补丁应用于当前状态。允许传递嵌套值。
$patch 允许两种参数传递方式,传入一个函数,或一个 state 的补丁。
/**
* $patch 函数传递方式
* @param stateMutation
* @example store.$patch((state) => state.count += 200);
*/
function $patch(stateMutation: (state: UnwrapRef<S>) => void): void;
/**
* $patch 对象传递方式
* @param partialState
* @example store.$patch({ count: 100 });
*/
function $patch(partialState: _DeepPartial<UnwrapRef<S>>): void;
function $patch(partialStateOrMutator: _DeepPartial<UnwrapRef<S>> | ((state: UnwrapRef<S>) => void)): void {
Log('$patch', partialStateOrMutator);
// 订阅收集器,保存收集到的订阅者
let subscriptionMutation: SubscriptionCallbackMutation<S>;
isListening = isSyncListening = false;
// 重置 debugger 事件,因为 patches 是同步的
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (__DEV__) {
debuggerEvents = [];
}
// 对两种传参方式进行兼容
// 如果参数是函数
if (typeof partialStateOrMutator === 'function') {
// 如果是函数,直接调用,并把 state 传过去
partialStateOrMutator(pinia.state.value[$id] as UnwrapRef<S>);
// 收集订阅,分别保存类型、id、事件
subscriptionMutation = {
type: MutationType.patchFunction,
storeId: $id,
events: debuggerEvents as DebuggerEvent[],
};
} else {
// 如果传来的是 object
// merge 参数对象到当前 store 的 state
mergeReactiveObjects(pinia.state.value[$id], partialStateOrMutator);
subscriptionMutation = {
type: MutationType.patchObject,
payload: partialStateOrMutator,
storeId: $id,
events: debuggerEvents as DebuggerEvent[],
};
}
//
const myListenerId = (activeListener = Symbol());
nextTick().then(() => {
if (activeListener === myListenerId) {
isListening = true;
}
});
isSyncListening = true;
// 在上方逻辑中,我们将 isListening isSyncListening 重置为 false,不会触发 $subscribe 中的 callback,所以需要手动进行订阅发布
triggerSubscriptions(subscriptions, subscriptionMutation, pinia.state.value[$id] as UnwrapRef<S>);
}
其中 triggerSubscriptions 方法是发布者,执行订阅函数的回调:
/**
* 触发订阅者回调
* @param subscriptions 订阅数组
* @param args 传给回调的参数
*/
export function triggerSubscriptions<T extends _Method>(subscriptions: T[], ...args: Parameters<T>) {
subscriptions.slice().forEach((callback) => {
callback(...args);
});
}
4. $reset
通过建立一个新的状态对象,将 store 重设为初始状态。
/**
* $reset
* 只有 选项式 构建的才可以使用此方法,
* 因为 state: () => ({count: 1}) 是一个函数,只要重新调用就可以获取原始值,
* 而 组合式 构建的话 state 以 ref() 的形式实现,无法获取原始值。
*/
const $reset = isOptionsStore
? function $reset(this: _StoreWithState<Id, S, G, A>) {
const { state } = options as DefineStoreOptions<Id, S, G, A>;
// 取出 options 中的 state 函数重新执行,以获取到原始 state
const newState = state ? state() : {};
// 使用 $patch 更新 state,并分发订阅
this.$patch(($state) => {
assign($state, newState);
});
}
: /* istanbul ignore next */
__DEV__
? () => {
// 如果是组合式语法构建的话,抛出错误,因为 ref() 不能获取到原始值
throw new Error(`🍍: Store "${$id}" is built using the setup syntax and does not implement $reset().`);
}
: // noop 是个空函数,生产环境不抛出错误
noop;
5. $subscribe
设置一个回调,当状态发生变化时被调用。它会返回一个用来移除此回调的函数。 请注意,当在组件内调用 store.$subscribe() 时,除非 detached 被设置为 true, 否则当组件被卸载时,它将被自动清理掉。
/**
* 当状态发生变化时被调用
* 它会返回一个用来移除此回调的函数
* @param callback 回调
* @param options 配置
* @returns 返回一个取消订阅的函数,调用次函数时订阅就被取消了
*/
function $subscribe(callback, options = {}) {
Log('$subscribe', options);
// 取消订阅函数
const removeSubscription = addSubscription(subscriptions, callback, options.detached, () => stopWatcher());
// effectScope:创建一个 effect 作用域,可以补货其中所创建的响应式副作用 (即计算属性和侦听器),这里用于捕获 watch,以便于销毁store的时候统一处理。
const stopWatcher = scope.run(() =>
// 从这里可以看出 pinia 的订阅响应式主要是依赖 vue 的 watch
watch(
() => pinia.state.value[$id] as UnwrapRef<S>,
(state) => {
if (options.flush === 'sync' ? isSyncListening : isListening) {
callback(
{
storeId: $id,
type: MutationType.direct,
events: debuggerEvents as DebuggerEvent,
},
state
);
}
},
assign({}, $subscribeOptions, options)
)
)!;
return removeSubscription;
}
其中, addSubscription 函数可以查看2. $onAction 。
6. $dispose
停止 store 的相关作用域,并从 store 注册表中删除它。 插件可以覆盖此方法来清理已添加的任何副作用函数。 例如, devtools 插件停止显示来自 devtools 的已停止的 store。
/**
* $dispose
* 停止 store 的相关作用域,并从 store 注册表中删除它。
* 插件可以覆盖此方法来清理已添加的任何副作用函数。 例如, devtools 插件停止显示来自 devtools 的已停止的 store。
*/
function $dispose() {
scope.stop();
subscriptions = [];
actionSubscriptions = [];
pinia._s.delete($id);
}
六、🧐源码分析(5)—— 辅助函数
Pinia 也提供了一组类似 Vuex 的 映射 state 的辅助函数。你可以用和之前一样的方式来定义 Store。这里不做使用的介绍,用法请看官网:https://pinia.vuejs.org/zh/introduction.html
🚪源码目录: src/pinia/mapHelpers.ts
1. mapActions
mapActions 有两种传参方式,两种传参方式第一个参数都是 defineStore 中返回的 useStore 函数。
- 传入一个对象,key 为映射到
methods中的名字,value 为 action 的名字。 - 传入一个数组,item 为 action 的名字。
下面是 mapActions 的源码,主要思想就是调用 useStore 方法得到 Store ,然后取出需要的 action 并返回。
/**
* 这个方法需要传入 useStore 和一个对象,可以在导入过程中给 action 改名,对象 key 为 action 的新名字,value 为 action 的旧名字
* 通过生成一个传递到组件的 methods 字段的对象, 允许直接使用 store 的 action,而不需要使用组合式 API(setup())。 该对象的值是 action, 而键是产生的方法名称。
*
* @example
* ```js
* export default {
* methods: {
* // other methods properties
* // useCounterStore has two actions named `increment` and `setCount`
* ...mapActions(useCounterStore, { moar: 'increment', setIt: 'setCount' })
* },
*
* created() {
* this.moar()
* this.setIt(2)
* }
* }
* ```
*
* @param useStore - defineStore 返回的 useStore
* @param keyMapper - 为 action 定义新名称的对象
*/
export function mapActions<
Id extends string,
S extends StateTree,
G extends _GettersTree<S>,
A,
KeyMapper extends Record<string, keyof A>
>(
useStore: StoreDefinition<Id, S, G, A>,
keyMapper: KeyMapper
): _MapActionsObjectReturn<A, KeyMapper>
/**
* 这个方法需要传入 useStore 和一个数组,数组内容为需要导入的 action 名称
* 通过生成一个传递到组件的 methods 字段的对象, 允许直接使用 store 的 action,而不需要使用组合式 API(setup())。 该对象的值是 action, 而键是产生的方法名称。
*
* @example
* ```js
* export default {
* methods: {
* // other methods properties
* ...mapActions(useCounterStore, ['increment', 'setCount'])
* },
*
* created() {
* this.increment()
* this.setCount(2) // pass arguments as usual
* }
* }
* ```
*
* @param useStore - defineStore 返回的 useStore
* @param keys - 要映射的 action 名称数组
*/
export function mapActions<
Id extends string,
S extends StateTree,
G extends _GettersTree<S>,
A
>(
useStore: StoreDefinition<Id, S, G, A>,
keys: Array<keyof A>
): _MapActionsReturn<A>
/**
* 通过生成一个传递到组件的 methods 字段的对象, 允许直接使用 store 的 action,而不需要使用组合式 API(setup())。 该对象的值是 action, 而键是产生的方法名称。
*
* @param useStore - defineStore 返回的 useStore
* @param keysOrMapper - array or object
*/
export function mapActions<
Id extends string,
S extends StateTree,
G extends _GettersTree<S>,
A,
KeyMapper extends Record<string, keyof A>
>(
useStore: StoreDefinition<Id, S, G, A>,
keysOrMapper: Array<keyof A> | KeyMapper
): _MapActionsReturn<A> | _MapActionsObjectReturn<A, KeyMapper> {
return Array.isArray(keysOrMapper)
// 如果传入的是数组,遍历这个数组取出所有 action 名称
? keysOrMapper.reduce((reduced, key) => {
// @ts-expect-error
reduced[key] = function (
// 如果组件的具体类型无法获得,或者你并不关心组件的具体类型,那么可以使用 ComponentPublicInstance
this: ComponentPublicInstance,
...args: any[]
) {
return useStore(this.$pinia)[key](...args)
}
return reduced
}, {} as _MapActionsReturn<A>)
// 如果传入的是对象,keysOrMapper[key] 值为 action 名称
: Object.keys(keysOrMapper).reduce((reduced, key: keyof KeyMapper) => {
// key 为新 name
// @ts-expect-error
reduced[key] = function (
this: ComponentPublicInstance,
...args: any[]
) {
return useStore(this.$pinia)[keysOrMapper[key]](...args)
}
return reduced
}, {} as _MapActionsObjectReturn<A, KeyMapper>)
}
2. mapStores
通过生成一个对象,传递到组件的 computed 字段 以允许在不使用组合式 API(setup()) 的情况下使用 store。 它接受一个 store 定义的列表参数。
/**
* 通过生成一个对象,传递到组件的 computed 字段 以允许在不使用组合式 API(setup())的情况下使用 store。 它接受一个 store 定义的列表参数。
*
* @example
* ```js
* export default {
* computed: {
* // other computed properties
* ...mapStores(useUserStore, useCartStore)
* },
*
* created() {
* this.userStore // store with id "user"
* this.cartStore // store with id "cart"
* }
* }
* ```
*
* @param stores - 要映射到 object 的 stores 列表
*/
export function mapStores<Stores extends any[]>(
// 所有参数放入 stores 数组,所以 store 不需要在包裹一层数组
...stores: [...Stores]
): _Spread<Stores> {
// 直接将 store 通过参数传递即可,不需要放到数组中,如果放到了数组中就抛出警告
if (__DEV__ && Array.isArray(stores[0])) {
console.warn(
`[🍍]: Directly pass all stores to "mapStores()" without putting them in an array:\n` +
`Replace\n` +
`\tmapStores([useAuthStore, useCartStore])\n` +
`with\n` +
`\tmapStores(useAuthStore, useCartStore)\n` +
`This will fail in production if not fixed.`
)
stores = stores[0]
}
// 遍历所有传进来的 useStore 并执行,然后 return 出去就得到了所有的 store
return stores.reduce((reduced, useStore) => {
// $id 是 defineStore 添加的
// @ts-expect-error: $id is added by defineStore
reduced[useStore.$id + mapStoreSuffix] = function (
this: ComponentPublicInstance
) {
return useStore(this.$pinia)
}
return reduced
}, {} as _Spread<Stores>)
}
3. mapState
通过生成一个对象,并传递至组件的 computed 字段, 以允许在不使用组合式 API(setup())的情况下使用一个 store 的 state 和 getter。 该对象的值是 state 属性/getter, 而键是生成的计算属性名称。 你也可以选择传递一个自定义函数,该函数将接收 store 作为其第一个参数。 注意,虽然它可以通过 this 访问组件实例,但它没有标注类型。
/**
* 通过生成一个对象,并传递至组件的 computed 字段, 以允许在不使用组合式 API(setup())的情况下使用一个 store 的 state 和 getter。 该对象的值是 state 属性/getter, 而键是生成的计算属性名称。 你也可以选择传递一个自定义函数,该函数将接收 store 作为其第一个参数。 注意,虽然它可以通过 this 访问组件实例,但它没有标注类型。
*
* @example
* ```js
* export default {
* computed: {
* // other computed properties
* // useCounterStore has a state property named `count` and a getter `double`
* ...mapState(useCounterStore, {
* n: 'count',
* triple: store => store.n * 3,
* // note we can't use an arrow function if we want to use `this`
* custom(store) {
* return this.someComponentValue + store.n
* },
* doubleN: 'double'
* })
* },
*
* created() {
* this.n // 2
* this.doubleN // 4
* }
* }
* ```
*
* @param useStore - defineStore 中返回的 useStore
* @param keyMapper - state 的属性名 或 getters 的对象
*/
export function mapState<
Id extends string,
S extends StateTree,
G extends _GettersTree<S>,
A,
KeyMapper extends Record<
string,
keyof S | keyof G | ((store: Store<Id, S, G, A>) => any)
>
>(
useStore: StoreDefinition<Id, S, G, A>,
keyMapper: KeyMapper
): _MapStateObjectReturn<Id, S, G, A, KeyMapper>
/**
* Allows using state and getters from one store without using the composition
* API (`setup()`) by generating an object to be spread in the `computed` field
* of a component.
*
* @example
* ```js
* export default {
* computed: {
* // other computed properties
* ...mapState(useCounterStore, ['count', 'double'])
* },
*
* created() {
* this.count // 2
* this.double // 4
* }
* }
* ```
*
* @param useStore - defineStore 中返回的 useStore
* @param keys - state 的属性名 或 getters 的数组
*/
export function mapState<
Id extends string,
S extends StateTree,
G extends _GettersTree<S>,
A,
Keys extends keyof S | keyof G
>(
useStore: StoreDefinition<Id, S, G, A>,
// key数组,内容仅限于 State 和 Getter 的 key
keys: readonly Keys[]
): _MapStateReturn<S, G, Keys>
/**
* Allows using state and getters from one store without using the composition
* API (`setup()`) by generating an object to be spread in the `computed` field
* of a component.
*
* @param useStore - defineStore 中返回的 useStore
* @param keysOrMapper - array or object
*/
export function mapState<
Id extends string,
S extends StateTree,
G extends _GettersTree<S>,
A
>(
useStore: StoreDefinition<Id, S, G, A>,
keysOrMapper: any
): _MapStateReturn<S, G> | _MapStateObjectReturn<Id, S, G, A> {
// 此处逻辑和 mapAction 很像
return Array.isArray(keysOrMapper)
? keysOrMapper.reduce((reduced, key) => {
reduced[key] = function (this: ComponentPublicInstance) {
// 和 mapAction 的区别:mapAction 取出的是经过 wrapAction 的 action ,然后在这调用了一下
return useStore(this.$pinia)[key]
} as () => any
return reduced
}, {} as _MapStateReturn<S, G>)
: Object.keys(keysOrMapper).reduce((reduced, key: string) => {
// @ts-expect-error
reduced[key] = function (this: ComponentPublicInstance) {
const store = useStore(this.$pinia)
const storeKey = keysOrMapper[key]
// 由于某种原因,TS 无法将 storeKey 的类型推断为函数
return typeof storeKey === 'function'
? (storeKey as (store: Store<Id, S, G, A>) => any).call(this, store)
: store[storeKey]
}
return reduced
}, {} as _MapStateObjectReturn<Id, S, G, A>)
}
4. mapGetters
mapGetters 已废弃,直接使用 mapState 即可。
/**
* Alias for `mapState()`. You should use `mapState()` instead.
* @deprecated use `mapState()` instead.
*/
export const mapGetters = mapState
5. mapWritableState
在使用 $mapState 把 state 导入 computed 时,如果直接去修改 state 的值是不允许的。
$mapWritableState ********除了创建的计算属性的 setter,其他与 mapState() 相同, 所以 state 可以被修改。 与 mapState() 不同的是,只有 state 属性可以被添加。
/**
* 除了创建的计算属性的 setter,其他与 mapState() 相同, 所以 state 可以被修改。 与 mapState() 不同的是,只有 state 属性可以被添加。
*
* @param useStore - store to map from
* @param keyMapper - object of state properties
*/
export function mapWritableState<
Id extends string,
S extends StateTree,
G extends _GettersTree<S>,
A,
KeyMapper extends Record<string, keyof S>
>(
useStore: StoreDefinition<Id, S, G, A>,
keyMapper: KeyMapper
): _MapWritableStateObjectReturn<S, KeyMapper>
/**
* Allows using state and getters from one store without using the composition
* API (`setup()`) by generating an object to be spread in the `computed` field
* of a component.
*
* @param useStore - store to map from
* @param keys - array of state properties
*/
export function mapWritableState<
Id extends string,
S extends StateTree,
G extends _GettersTree<S>,
A,
Keys extends keyof S
>(
useStore: StoreDefinition<Id, S, G, A>,
keys: readonly Keys[]
): {
[K in Keys]: {
get: () => S[K]
set: (value: S[K]) => any
}
}
/**
* Allows using state and getters from one store without using the composition
* API (`setup()`) by generating an object to be spread in the `computed` field
* of a component.
*
* @param useStore - store to map from
* @param keysOrMapper - array or object
*/
export function mapWritableState<
Id extends string,
S extends StateTree,
G extends _GettersTree<S>,
A,
KeyMapper extends Record<string, keyof S>
>(
useStore: StoreDefinition<Id, S, G, A>,
keysOrMapper: Array<keyof S> | KeyMapper
): _MapWritableStateReturn<S> | _MapWritableStateObjectReturn<S, KeyMapper> {
// 也是对于数组和对象的分别处理
// 返回包含 get 和 set 函数的对象,交给 computed 处理
return Array.isArray(keysOrMapper)
? keysOrMapper.reduce((reduced, key) => {
// @ts-ignore
reduced[key] = {
get(this: ComponentPublicInstance) {
return useStore(this.$pinia)[key]
},
set(this: ComponentPublicInstance, value) {
// it's easier to type it here as any
return (useStore(this.$pinia)[key] = value as any)
},
}
return reduced
}, {} as _MapWritableStateReturn<S>)
: Object.keys(keysOrMapper).reduce((reduced, key: keyof KeyMapper) => {
// @ts-ignore
reduced[key] = {
get(this: ComponentPublicInstance) {
return useStore(this.$pinia)[keysOrMapper[key]]
},
set(this: ComponentPublicInstance, value) {
// it's easier to type it here as any
return (useStore(this.$pinia)[keysOrMapper[key]] = value as any)
},
}
console.log(reduced)
return reduced
}, {} as _MapWritableStateObjectReturn<S, KeyMapper>)
}
✨结语
代码虽然比较多,但核心逻辑还是借助 vue 的 ref 和 reactive 实现响应式。把 state 处理为 ref ,把 getters 处理成 computed ,提供一些基础方法,并使用单例模式返回一个实例。
完整注释代码: